Climate Resilience



Key Performance in 2024
Received an B rating or equivalent Management Level from CDP for climate change
Reduction GHG emissions from emission reduction projects
Absorbed through community and social engagement in greenhouse gas reduction awareness programs, such as tree planting projects
Key Progress in 2024

Set a net-zero greenhouse gas emissions target and submitted the target for validation under the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi). The target is currently under review by SBTi

Communicated the climate change strategic plan and roadmap towards achieving carbon neutrality by 2030 to relevant departments as a guideline for further development

Participated in the CDP climate change program for the 6th consecutive year

Assessed climate change risks following the reporting framework of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)

Engaged with suppliers and customers to reduce environmental impacts, such as developing low-carbon products and educating suppliers on greenhouse gas accounting
Supporting the SDGs

SDG 12 Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
12.2 Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources

SDG 13 Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
13.1 Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries
Performance Against Goal
Results of the “Double Materiality Matrix”
Sustainable Dimension
Impact level for application in business operations
Progress against Short-term and Long-Term Goals
To achieve Carbon Neutral by 2030 and Net Zero GHG Emissions by 2050
Performance Summary 2024
Total GHG Emissions by scope of operation
CP ALL and Subsidiaries
Direct GHG emissions (Scope 1)
Indirect GHG emissions from energy Consumption (Scope 2)
Indirect GHG emissions (Scope 3)
Only CP ALL
Direct GHG emissions (Scope 1)
Indirect GHG emissions from energy Consumption (Scope 2)
Indirect GHG emissions (Scope 3)
Total GHG Emission by sources
CP ALL and Subsidiaries
Electricity purchased externally
Diesal
Benzene
Natural gas and Liquefied Petroleum gas
Biofuel combustion
Refrigerant
Methane from the wastewater treatment system
Only CP ALL
Electricity purchased externally
Diesal
Benzene
Natural gas and Liquefied Petroleum gas
Biofuel combustion
Refrigerant
Total GHG Emission by per energy purchases GHG emissions (Scope 2)
Location-Based
Data Coverage (as % of Denominator)
Market-Based
Data Coverage (as % of Denominator)
GHG Emissions Intensity (Scope 1 and Scope 2) per Unit of Revenue
The amount of ruduction from implementing a greenhouse gas emission reduction project
Energy efficiency improvement
Renewable energy utilization
Remark: Utilization of renewable energy comprises of electricity from solar energy, solar thermal energy and geothermal energy
The use of eco-friendly refrigerants
Electric vehicles in logistics
Reduction and absorption of GHG from the Supply Chain
Support society and communities to be aware of reducing GHG emissions (from tree planting projects)
Donating excess surplus food
Usage of single-use plastic packaging
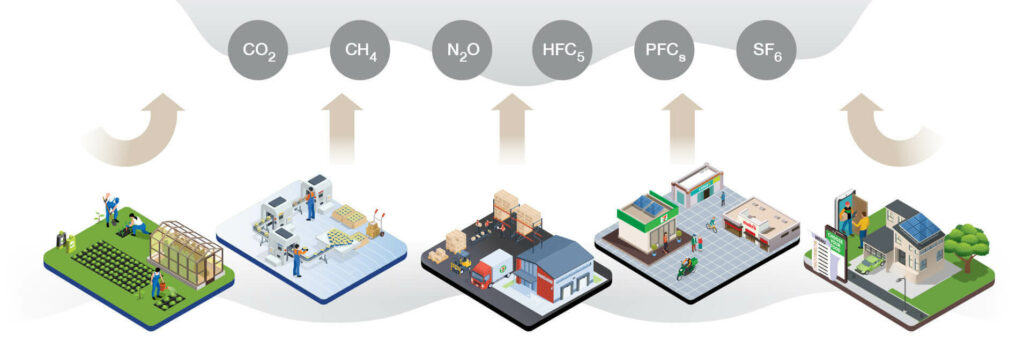
Other Indirect GHG Emissions by category (tCO2e)
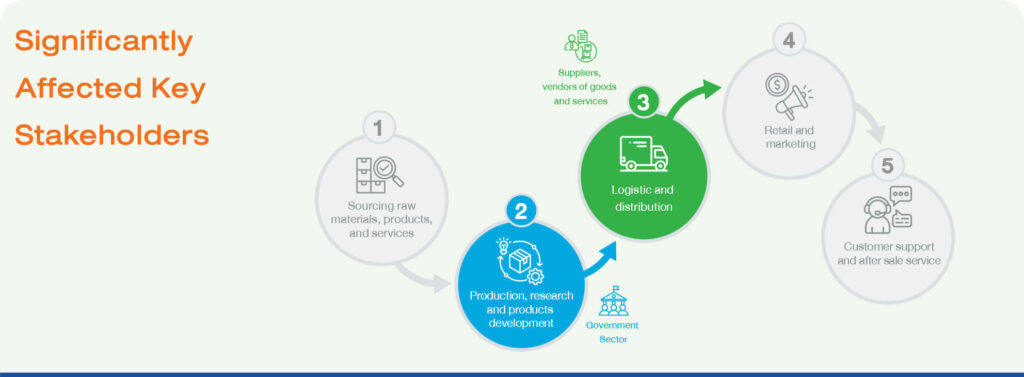
Upstream activities

Purchased Goods and Service
Capital Goods
The acquisition of fuel and energy by the organization

Upstream Transportation and Distribution

Waste Generated in Operations

Business Travel

Employee Commuting
Downstream activities
Downstream Transportation and Distribution

Use of sold products

End-of-Life Treatment of Sold Products

Downstream Leased Assets
Risks and Opportunities
The 29th United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP29) in 2024 is being held in Baku, Azerbaijan, focusing on strengthening financial mechanisms for climate change and supporting vulnerable communities. The discussions aim to address environmental, economic, and long-term human livelihood impacts and work toward establishing a New Collective Quantified Goal on Climate Finance (NCQG) to support efforts in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The key discussion points include: 1) the implementation of the Loss and Damage Fund to support affected communities, particularly in Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs); 2) strengthening national commitments, with countries expected to submit updated plans by 2025 and advance their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs); 3) the allocation of financial operation funds, targeting $1 billion per year to support renewable energy and climate restoration in developing countries, alongside discussions on financial mechanisms for adaptation and mitigation; 4) the role of various sectors, particularly the private sector, in transitioning to renewable energy and developing innovative financing models. Special sessions are also being held on key topics such as land-use industries, water management, and just transition strategies to ensure a sustainable and equitable approach to climate action; 5) the role of global dynamics, leadership from civil society, the business sector, and local governments in achieving an equitable future with resilience and net-zero carbon emissions. This aims to achieve the Paris Agreement, National Adaptation Plans (NAPs), and Biennial Transparency Reports (BTRs), emphasizing the goal of limiting global surface temperature rise to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius. The mission is crucial to recognize the need for a 43% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and a 60% reduction by 2035. Climate change poses a threat to human rights in health and livelihoods, access to food, clean water, fresh air, and safe housing, as well as leading to the degradation of ecosystems.
In addition, transition risks related to climate change, such as climate-related regulations and natural disaster response, may impact the business and industrial sectors. The Company recognizes the impact of business activities that contribute to climate change and focuses on implementing projects to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, supporting environmentally friendly operations, and responding to market demand for eco-friendly products and services. Furthermore, the Company prepares for risks and develops sustainability policies.
Management Approach
The Company is committed to conducting business sustainably and supporting efforts to limit the global temperature increase to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius through three key measures: 1) Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, such as improving energy efficiency, minimizing energy losses, increasing the proportion of renewable energy use, and adopting environmentally friendly refrigerants. 2) Carbon absorption and credit purchases, such as forest restoration and purchasing carbon credits to offset emissions. 3) Eliminating energy waste/loss, including initiatives to encourage employees to conserve energy. Additionally, the Company prioritizes collaboration with suppliers to transition to environmentally friendly packaging throughout the value chain, promotes reusable products, and encourages consumers to reduce single-use packaging. The Company also supports the participation of all stakeholders in achieving climate change goals. The Company has established a Sustainability Development Subcommittee to oversee climate action and designated specialized teams, such as the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Team, Solar Energy Installation Team, and Eco-Friendly Packaging Development Team, to manage climate-related operations. Under the “7 Go Green” policy, the Company focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from business operations in alignment with the goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2030 and striving for complete net-zero emissions by 2050. The Company manages greenhouse gas emissions in three categories: Direct Emissions (Scope 1), Indirect Emissions from energy use (Scope 2), and Other Indirect Emissions (Scope 3). Furthermore, the Company has set a net-zero greenhouse gas emission target based on the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) and has established a framework and guidelines for responsible climate action across the entire supply chain.
The company's targets have now been validated by the SBTI.
Near-term targets aligned with SBTi as follow:
| Scope covered by the target | Target Time frame | Baseline year emissions covered and as a % of total base year emission | % reduction target from base year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 and Scope 2 |
|
|
42 |
| Scope 3 |
|
|
25 |
Net Zero Commitment aligned with SBTi as follow:
Climate Change Management Framework
Commitment
to minimize impacts according to laws and regulations, and the UN SDGS
Risk and Opportunity Assessment
of Climate Change is integrated into the Company’s enterprise risk assessment, both in top-down and bottom-up management, using the TCFD framework
Establishment of Policy
Goals and Strategy in reducing emissions and installing countermeasures throughout the business’ value chain
Execution
through multiple projects under the “7 Go Green” Strategy in 4 aspects
Assessment and Evaluation
refers to monitoring of progress against targets and analysis to identify improvement approaches on a quarterly basis by the sustainable development sub-committee
Communication with Stakeholders
refers to strategy and its respective execution, as well as collaboration with stakeholders and progress

Corporate Climate governance
The Company continuously conducts materiality assessments to analyze issues of stakeholder interest. The assessment results are integrated into the Company's strategic plan, highlighting that climate change is ranked as a highly significant issue. As a result, various management and mitigation activities have been implemented, such as strategic planning, transition planning, long-term target setting, risk assessment, and supply chain management, with reports submitted to the governing body according to the corporate governance structure.
CP ALL evaluates the climate change capabilities of the Board of Directors by considering their experience in climate-related issues. The CP ALL board members possess expertise in climate-related matters due to their experience in overseeing sustainability and climate governance across multiple publicly listed companies as board members. Additionally, they serve as the Chairperson of the Global Compact Network Thailand, which is the national chapter of the United Nations Global Compact in Thailand.
Management System for Lobbying Activities, Trade Association Membership, and Public Policy Engagement on Climate Change
To align with the Company's Climate Change Action Framework, the Company has joined the Thailand Carbon Neutral Network (TCNN) to drive and support sustainable development goals across the private sector, government, and local communities. TCNN was established by the Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (Public Organization) with a mission to promote greenhouse gas reduction projects and advance toward net-zero greenhouse gas emissions, in line with the Paris Agreement. The network's development objectives are as follows:
Experts and advisors collaborate and provide guidance on corporate climate change management during meetings between network members and the subcommittee to discuss strategies and operational plans. These meetings also include discussions on policy support for greenhouse gas reduction and seeking government support. During these meetings, the Company actively contributes CP ALL perspectives, engages in discussions on various topics, and continues to support association activities.
The Company and executives responsible for sustainability policy oversight regularly monitor the progress of the Thailand Carbon Neutral Network's mission. This ensures awareness of developments, facilitates participation in discussions, and drives climate change management initiatives. Additionally, the Company aligns the policies with national climate strategies.
Additionally, the Company is a co-founding member of the Global Compact Network Thailand (GCNT), aiming to achieve sustainability goals, including carbon neutrality and net-zero greenhouse gas emissions. The Company, in collaboration with the association, drives the commitment of private sector and civil society organizations while also sharing best practices for achieving carbon neutrality and net-zero emissions.
Describe the Board’s Oversight of Climate-related Risks and Opportunities
| Governing Body | Roles and Responsibilities | Meeting Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
Sustainability and Corporate Governance Committee (Board-level Committee) |
Sustainability and Corporate Governance Committee is chaired by an independent director from the Board of Director. The Committee members include the Chairman of Audit committee, the Chairman of Remuneration and Nomination Committee and a member of Executive Committee. Quarterly meetings are scheduled for the Committee in order update and discuss on sustainability performance including climate change topic and report to the Board of Director at least twice a year. As an annual process, the Committee reviewing and guiding annual budgets overseeing major capital expenditures, guiding employee incentives, reviewing and guideline climate strategy, overseeing and guiding the development of a transition plan, overseeing and guiding public policy engagement and reviewing and guiding the risk management process related to Climate issues. the Committee takes climate-related roles and responsibilities according to its charter as follows; 1) Frame policy and guideline on promoting innovation, environmental social responsibility (including climate change topic), and sustainable development plan |
Quarterly |
|
Sustainability Sub-Committee |
Developing a climate transition plan Implementing a climate transition plan Integrating climate-related issues into the strategy Setting climate-related corporate targets Monitoring progress against climate-related corporate targets Assessing climate-related risks and opportunities Sustainable Development Sub-Committee as an important mechanism in driving processes and ensuring that executives and employees of the Company and its subsidiaries correctly and completely understand and earnestly practice business ethics and sustainable development of the organization. This is considered part of the Company’s organizational culture that the top management has established as the corporate governance observance that is one of the organization’s strategies and objectives. Both sub-committees must report to the Sustainability and Corporate Governance Committee every quarter .Responsibilities of the Sub-Committee include; |
Quarterly |
|
Risk Management Committee |
The Risk Management Committee has the following roles and responsibilities: 1.Review and refine draft risk management policies and frameworks before presenting them to the Board of Directors |
Quarterly |
|
Corporate Sustainability Management Division |
environmental management acts as a focal point in coordinating with relevant functions to monitor climate-related topics, at monthly to yearly interval depending on the nature of topics. The results are reported to the Committee at least semi-annually. Additionally, climate-related data will be consolidated annually and presented to the Sustainability and Corporate Governance Committee for reviewing as part of sustainability reporting process. The involvement of top managements across the entire organization in this Sub Committee makes it a robust platform to exchange information, discuss key climate topics, form mutual commitments, and collaborate towards the goals. |
Monthly |
Climate-Related Management Incentives
| details on the climate change-related incentives starting from the highest management level | Incentivized KPIs |
| Chief Executive Officer (CEO) One of the goals that indicates a special bonus for the CEO is achieving great scores on the Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI), which evaluates the effectiveness of the company's operations in accordance with its sustainable development objectives. |
Overall sustainability program’s performance including the climate performance (Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI) scores) is one of the CEO’s KPIs. |
| Executives Officers: Example 1.Senior Vice President, Corporate Asset and Facilities Management is entitled to monetary incentive from energy efficiency management. His KPI is directly tied with over all facilities’ store energy reduction with 10% weight. The SVP is also responsible for driving innovative energy management at stores and increasing proportion of renewable energy in energy portfolio. The SVP also leads energy conservation committee whose KPIs are tied with “energy reduction and efficiency performance” cascaded from the Corporate Sustainability KPIs. 2.Assistant Vice President, Social and Environmental Management is entitled to monetary incentive from GHG emissions reduction. His KPI is directly tied with over all GHG emissions reduction and Promote Green product with 40% weight. The AVP is also responsible for driving innovative GHG emission management. The AVP also leads 7 Go Green committee whose KPIs are tied with “Carbon Neutral by 2030 and Net Zero GHG Emissions by 2050” cascaded from the Corporate Sustainability KPIs. The KPIs of other executives are also tied with a pool of KPIs that links with Corporate Sustainability KPIs to drive performances across functions. |
Overall facility store energy reduction is weighted 10% for Senior Vice 1.President of Corporate Asset and Facilities Management department. Moreover, energy reduction and efficiency performance are also the KPIs of our Energy Conservation Committee. The target and goal have been cascaded and collaborated with other functions i.e. purchasing department and operation department. 2.Overall facilityGHG emissions and Promote Green product is weighted 40% for Assistant Vice President of Social and Environmental Management department. Moreover, GHG emissions and Promote Green product performance are also the KPIs of our 7 Go Green Committee. The target and goal have been cascaded and collaborated with other functions i.e. purchasing department and operation department. |
| Business Unit Managers: Example
1.Business Unit Managers are entitled to monetary incentive from energy reduction and efficiency performance. Their KPIs i.e. energy reduction and efficiency performance are cascaded from the Corporate Sustainability KPIs. Furthermore, Business Unit Managers who take part in Energy Conservation Committee also have the KPI directly tied with Corporate Sustainability Score (derived from DJSI score). 2.Business Unit Managers are entitled to monetary incentive from GHG emissions reduction performance. Their KPIs i.e. GHG emissions reduction performance are cascaded from the Corporate Sustainability KPIs. Furthermore, Business Unit Managers who take part in 7 Go Green Committee also have the KPI directly tied with Corporate Sustainability Score (derived from DJSI score). |
1.Achievement of individual KPIs on “energy reduction and efficiency performance” will contribute to the incentives of Business Unit Managers. Furthermore, if the energy reduction and efficiency performance targets are achieved, members of the Energy Conservation Committee will also be rewarded with monetary incentive. 2.Achievement of individual KPIs on “GHG emissions reduction performance” will contribute to the incentives of Business Unit Managers. Furthermore, if the GHG emissions reduction performance targets are achieved, members of the 7 Go Green Committee will also be rewarded with monetary incentive. |
Climate Risk Management
The Company is committed to addressing risks and opportunities associated with potential climate change. An appointment organization risk assessment committee is tasked with evaluating risk factors and impacts, including opportunities related to climate change which may affect business operations. The assessment results require approval by the Sustainability and Corporate Governance Committee prior to Company disclosure of climate risk management information to stakeholders in accordance with the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD) framework. This approach enables the formation of an effective climate change risk plan.
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure: TCFD
In 2024, the Company has identified critical risk and opportunities, both physical risk and transition risks, associatied with climate change. Countermeasures to the mentioned risk include the following:
Physical Risks
| Risk | Impact to Value chain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
 Impact to the Business Impact to the Business |
 Impact to the Value Chain Impact to the Value Chain |
Short Term | Medium Term | Long Term |
|
|
Medium | High | High | |
 Mitigation Measures Mitigation Measures |
|||||
|
The Company has designed the structure of 7-Eleven stores to withstand flood damage under the “Flood Resistant Store” concept. This includes design considerations such as elevated barriers, specialized flooring and door designs to withstand water pressure, drainage systems, and water pumps. However, in the event of flooding, the Company has established an operational response plan divided into three phases of incident management:
|
|||||
|
|
 Impact to the Business Impact to the Business |
 Impact to the Value Chain Impact to the Value Chain |
Short Term | Medium Term | Long Term |
|
|
Low | Low | Medium | |
 Mitigation Measures Mitigation Measures |
|||||
|
|||||
Transition Risks
| Risk | Impact to Value chain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
 Impact to the Business Impact to the Business |
 Impact to the Value Chain Impact to the Value Chain |
Short Term | Medium Term | Long Term |
|
|
Medium | High | High | |
 Mitigation Measures Mitigation Measures |
|||||
|
The Company has been implementing the Plastic Waste Management Roadmap from 2018 to 2030, applying the framework of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) to reduce plastic pollution and minimize the use of single-use plastic bags. This is achieved through strategic initiatives for sustainable packaging and plastic waste management across the product lifecycle, including: development of innovative production and design technologies based on the Eco-Design concept; adoption of reusable packaging in line with the circular economy; take-back programs for packaging recovery; recycling projects; and consumer awareness campaigns to reduce and eliminate single-use plastics. Additionally, the Company promotes sustainable plastic waste management among supply chain partners by providing knowledge and supporting the implementation of EPR principles in their operations. |
|||||
|
|
 Impact to the Business Impact to the Business |
 Impact to the Value Chain Impact to the Value Chain |
Short Term | Medium Term | Long Term |
|
|
Low | Medium | Medium | |
 Mitigation Measures Mitigation Measures |
|||||
|
The organization has conducted a detailed study of the Climate Change Act, focusing on analyzing its impact on production processes and operations, as well as identifying potential risks. Based on this analysis, an action plan has been developed to mitigate impacts and create business opportunities. The key measures include:
|
|||||
|
|
 Impact to the Business Impact to the Business |
 Impact to the Value Chain Impact to the Value Chain |
Short Term | Medium Term | Long Term |
|
|
Low | Medium | Medium | |
 Mitigation Measures Mitigation Measures |
|||||
|
|||||
|
|
 Impact to the Business Impact to the Business |
 Impact to the Value Chain Impact to the Value Chain |
Short Term | Medium Term | Long Term |
|
|
Medium | Medium | High | |
 Mitigation Measures Mitigation Measures |
|||||
|
|||||
The 7 Go Green policy for 24-hour environmental sustainability
The policy has the aim to enhance environmental sustainability for communities, society, and the nation. This is achieved through various initiatives such as reducing energy consumption, increasing the proportion of renewable energy use, adopting environmentally friendly refrigerants, optimizing transportation and distribution systems, and transitioning to eco-friendly packaging. Additionally, the policy encourages consumer and community collaboration by fostering sustainable consumption habits through behavioral changes, reducing and eliminating plastic usage, and promoting plastic waste segregation. These efforts contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and raising environmental awareness within communities. The policy applies to 7-Eleven stores, Makro distribution centers, Lotus's, and CPRAM manufacturing plants. The Company also maintains transparency in environmental performance reporting to stakeholders through the Climate Change Disclosure Project (CDP), aligning with the Carbon Neutrality Roadmap (2024-2030). In 2024, CP ALL introduced the Sustainability Framework 2024-2025 (CP ALL Sustainability Framework) under the concept of "2 Reductions, 4 Creations, 1 DNA", reinforcing the commitment to being a community-centered organization that fosters sustainable social development. This framework integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles throughout the business value chain. Under the 7 Go Green policy for 24-hour environmental sustainability, the Company has outlined 4 key eco-friendly initiatives, as follows:

1. Green Store
Environmentally friendly store management

2. Green Logistic
Environmentally friendly logistics and distribution

3. Green Packaging
Environmentally friendly packaging management

4. Green Living
Build environmental consciousness
1. Operations of environmentally friendly stores and distribution centers (Green Store)
The Company aims to achieve a balance between conservation and the sustainable use of resources, integrating renewable energy into building design and construction. The Company also enhances the efficiency of electrical systems and equipment to be environmentally friendly, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This initiative covers 7-Eleven stores, Makro distribution centers, Lotus's, and CPRAM manufacturing plants. In 2024, the Company is implementing strategic projects under 4 key approaches, as follows:
1. Improve energy efficiency

2. Increase the proportion of renewable energy use

3. Use environmentally friendly refrigerants
4. Raise awareness and encourage behavioral changes among employees
Impacts and Benefits

Reduced energy consumption
Reduced GHG emissions
2. Environmentally Friendly Product Transportation (Green Logistic)
The Company is committed to developing green logistics by implementing environmentally friendly transportation management strategies. The focus is on reducing the environmental impact of logistics activities, such as lowering greenhouse gas emissions, reducing energy consumption, and improving transportation efficiency through optimized route planning. In 2024, the Company is implementing strategic projects under 4 key approaches, as follows:

1. Improve energy efficiency

2. Increase the proportion of renewable energy use
3. Promote green transportation systems
4. Use environmentally friendly vehicles
Impacts and Benefits

Reduced energy consumption

Reduced GHG emissions
3. Environmentally friendly packaging management (Green Packaging)Environmentally friendly packaging management (Green Packaging)
Green packaging is a key concept for the Company, aimed at promoting sustainability and differentiation to meet consumer demand while demonstrating social and environmental responsibility by reducing waste. The Company’s packaging management plan covers all stages, including design, usage, distribution to consumers, disposal, and recycling, ensuring that both environmental factors and customer needs are considered. Additionally, the Company promotes natural resource conservation throughout the supply chain. In 2024, the Company is implementing strategic projects under 3 key approaches, as follows:
1. Reduce plastic consumption at source

2. Reduce and replace single-use plastic at consumption point
3. Reduce post-consumer packaging waste
Impacts and Benefits

Eduction of virgin plastic volumes used in packaging production

Plastic packaging made from recycled materials

Reduction from single-use plastic consumption

GHG emissions reduction from reducing plastic use

Take Back for recycled
Recycled post-consumer packaging
4. Creating consciousness for environmental protection (Green Living)
The Company is committed to promoting environmental awareness, recognizing environmental challenges, and working collaboratively to address them. This is achieved through partnerships with customers, communities, NGOs, government agencies, and both international and local organizations. Various projects are implemented to raise environmental awareness within communities, contributing to improved and sustainable livelihoods. In 2024, the Company is implementing strategic projects under 4 key approaches, as follows:

1. Create awareness to shift consumption behaviors

2. Reduce food surplus with Food to Merit project
3. Reduce waste, enhance benefits of waste segregation, collection, and recycling

4. Increase green space, protect, and restore ecosystems
Impacts and Benefits
Waste sorting points nationwide

Reduce food waste to land fill

Donated over

Reduced GHG emissions

The Accumulated number of trees Planted
From the project to reduce impacts on the ecosystem on both land and water
Development and Sourcing of Low-Carbon Products
CPRAM Co., Ltd. And CP ALL Public Company Limited supports environmentally friendly products and places great importance on reducing GHG emissions in production. This is achieved by evaluating emissions and GHG reductions from each product throughout the product life cycle. All steps are evaluated starting from the procurement of raw materials, product processes, delivery, usage and disposal. In addition, its carbon footprint has been registered with the Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (Public Organization) (TGO).
In 2024, the Company registered 4 products under the Carbon Footprint Product Label, including: vegetarian basil rice; spicy basil rice; spicy bamboo shoot chicken fried rice; and chinese kale fried rice with salted fish. Additionally, 1 product, pork basil rice, was registered under the Carbon Footprint Reduction Label, generating sales of over 425 million Baht.
Community and Social Support for GHG Reduction
CP ALL has launched various initiatives to support communities and society in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, including: The “Love Trees, Care for the Environment” project, which involves measuring carbon sequestration of trees; donating an eco-friendly multipurpose sports field made from recycled plastic waste to Ban Nam Yoi School in Lamphun Province; and organizing beach clean-up activities in the wave barrier area of Khlong Yai District, Trat Province, encouraging community participation in recycling waste collected from the environment.
Impacts and Benefits

Reduced food waste sent to landfills

educed greenhouse gas emissions
Environmental Awareness and Education Communication Project
The Company has implemented communication and awareness initiatives on energy conservation, environmental protection, and climate change for executives, office employees, operations staff, logistics personnel, and affiliated companies within CP ALL Group. These initiatives aim to foster environmental consciousness and contribute to sustainable well-being for communities. The program leverages both offline and online communication channels to proactively disseminate environmental knowledge through various media platforms, such as:


In 2024, CP ALL provided training to 204,701 employees nationwide to promote understanding of sustainability. Additionally, an assessment of employees' awareness and understanding of sustainability at all levels found that 100% had knowledge and comprehension of the subject.
Management System for Lobbying Activities and Trade Association Memberships - Climate change
Thailand Carbon Neutral Network (TCNN)
In alignment with the organizational climate change action framework, the Company’s membership at the Thailand Carbon Neutral Network (TCNN), an initiative by the Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (Public Organization), signifies drive and support for sustainable development goals between the private, public, and local sectors. The mission to promote greenhouse gas emissions reduction, with aims for net zero emissions in accordance with the Paris Agreement, upholds the following mission:
Experts and consultants collectively cooperate and provide advice regarding organizational climate change management. In January 2023, Carbon Neutral Thailand Network organized the first conference between members and subcommittees to discuss network strategies and operational plans inclusive of support for greenhouse gas emissions reduction and government support requests. The Company actively participates in providing suggestions and interest in various support activities and topics raised within the conference.
The Company and executives tasked with corporate sustainability policy management regularly monitors mission progress with the Carbon Neutral Thailand Network. The joint effort facilitates opinions expression, national agenda for climate change management developments, and modification of organizational policies to maintain consistency with national policies.
Department of Climate Change and Environment, Pollution control department, Ministry of Natural resources and environment
Department of Climate Change and Environment was founded to promote, share and communicate to raise awareness and engagement in matters relating to the environment, human capacity development, engagement process and network in environmental quality promotion
Pollution Control Department was founded to manage, control, govern and protect the environment
Furthermore, the Company also participates as one of the founding members of the Global Compact Network Thailand (GCNT) with the aim to achieve sustainability goals, including carbon neutrality and net-zero greenhouse gas emissions. The Company collaborates with GCNT to support the advocacy from the private sector and civil society organizations. This also includes exchanging best practices in pursuing carbon neutrality and net zero greenhouse gas emissions goals.
Other Information
Taxonomy
Thailand is making strides towards environmental sustainability through the development of a Sustainability Taxonomy Framework (Thailand Taxonomy). The objective is to classify activities as environmentally-friendly, with a focus on reducing disparities in each sector's ability to transition towards environmental sustainability. Climate change mitigation is the primary environmental objective, and the framework will consider transparent conditions and indicators that are in line with Thailand businesses' early-stage status and ability to adopt.
The Thailand Taxonomy Board will issue specific details for each economic sector gradually, depending on necessity and urgency, taking into account each sector's potential impact and readiness to adapt. The Energy and Transportation sectors will be classified in the beginning phase. For later phases, it is planned that further specific details for the Agricultural, Industrial, and other economic sectors will be issued. Meanwhile, the Thailand Taxonomy will also focus on achieving consistency with the ASEAN taxonomy and comparability to other standards of other countries in the ASEAN region.
However, as CPALL is Food & Staples Retailing sector, we are willfully waiting for an updated from Bank of Thailand (BOT) who conducted the Thailand Taxonomy Board, and aims to establish a principle-based taxonomy in other phases which’s includes Food & Staples Retailing sector.
See more information: detail of Thailand Taxonomy Framework in Bank of Thailand website : https://app.bot.or.th/landscape/en/green/directions/taxonomy/
Related Policy and Guideline
| CDP Report 2025 | Download |
Other Information
Performance Data of Climate Resilience
| GRI Standard | Required Data | Unit | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 305-2 (a) | Total GHG emissions | tCO2e | 1,431,181.28 | 1,808,509.72 | 1,778,726.26 | 1,936,757.61 |
| 305-1 (a) | Direct (Scope 1) GHG emissions | tCO2e | 214,860.15 | 236,045.11 | 324,357.53 | 435,377.38 |
| - Fugitive Emissions | tCO2e | 176,066.41 | 194,989.93 | 277,558.52 | 384,212.73 | |
| - Methane from wastewater treatment | tCO2e | 3,742.42 | 819.66 | 1,230.88 | 556.81 | |
| - Stationary combustion | tCO2e | 25,468.24 | 30,428.86 | 29,598.88 | 30,645.31 | |
| - Mobile combustion | tCO2e | 9,021.92 | 9,253.95 | 14,834.57 | 18,575.28 | |
| 305-1 (c) | - Biogenic combustion | tCO2e | 579.15 | 552.71 | 1,134.68 | 1,387.26 |
| 305-2 (a) | Indirect (Scope 2) GHG emissions | tCO2e | 1,216,421.13 | 1,572,464.61 | 1,454,368.73 | 1,501,380.23 |
| - Electricity purchased | tCO2e | 1,216,421.13 | 1,572,464.61 | 1,454,368.73 | 1,501,380.23 | |
| GHG reduction from alternative energy consumption | tCO2e | 2,491.45 | 11,851.72 | 31,149.16 | 53,982.19 | |
| 305-4 (a) | Direct and indirect (Scope 1 andScope 2) per revenue unit | tCO2e per million Baht | 2.51 | 3.31 | 3.03 | 2.27 |
| 305-3 (a) | Other indirect (Scope 3) GHG emissions | tCO2e | 208,627.65 | 243,095.87 | 13,131,498.28 | 13,191,694.60 |
| - Purchase goods and service | tCO2e | N/A | N/A | 12,824,060.79 | 12,525,820.40 | |
| - capital goods | tCO2e | N/A | N/A | N/A | 47,305.39 | |
| - Upstream transportation and distribution | tCO2e | 90,128.25 | 141,122.76 | 197,321.23 | 268,798.35 | |
| - Waste generated in operations | tCO2e | 192,510.20 | 90,956.37 | 99,866.65 | 90,303.47 | |
| - Business travel (by planes) | tCO2e | 2,588.75 | 793.62 | 141.14 | 2,077.74 | |
| - employee travel | tCO2e | N/A | N/A | N/A | 153,865.70 | |
| - Downstream transportation and distribution | tCO2e | N/A | N/A | N/A | 94,192.64 | |
| - End-of-life treatment of sold products (Golden banana) | tCO2e | 13,528.70 | 10,226.12 | 10,108.25 | 9,330.91 | |
| GHG reduction from decreased consumption of single use plastic bag | tCO2e | 33,222.39 | 85,212.55 | 265,268.48 | 250,615.62 | |
| Percentage of the stores that have been designed or renovated for mitigating flood comparing to total store locating in flood risk areas | Percentage | N/A | N/A | 52 | 52 |




















