Responsible Supply Chain Management




Key Performance in 2024
of Tier-1 and Critical Non-tier 1 suppliers have completed risk screening
of Significant Tier-1 Suppliers and Non Tier-1 Suppliers have completed the assessment
of Significant Suppliers evaluated to pose negative ESG impact have devised a corrective action plan
of Significant Suppliers evaluated to pose negative ESG impact have received capacity development to improve ESG practices and performance
Key Progress in 2024

Improve the proactive sustainability supplier assessment model to align with international standards, covering risks by industry, business size and product

Promote knowledge and support SMEs to join the Private Sector Anti-Corruption Coalition (CAC) project

Conduct training for Critical Tier 1 Suppliers on greenhouse gas accounting

Promote capacity building of construction and transportation contractors to improve ESG practices and performance

Collaborate with suppliers on sustainability initiatives, encouraging participation in programs to eliminate shrink film usage and reduce greenhouse gas emissions

Implement the “Safe Oranges, Smiling Thais” project for the 10th year, promoting the elimination of chemical pesticides in favor of locally sourced herbal alternatives
Supporting the SDGs

SDG 4 Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
4.4 Substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship

SDG 8 Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
8.3 Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services

SDG 12 Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
12.7 Promote public procurement practices that are sustainable, in accordance with national policies and priorities
Performance Against Goal
Results of the “Double Materiality Matrix”
Sustainability dimension
Impact level for application in business operations
Progress against short-term and long-term goals
Significant Tier-1 Suppliers must be assessed and receive development and improvement
Performance Summary 2024
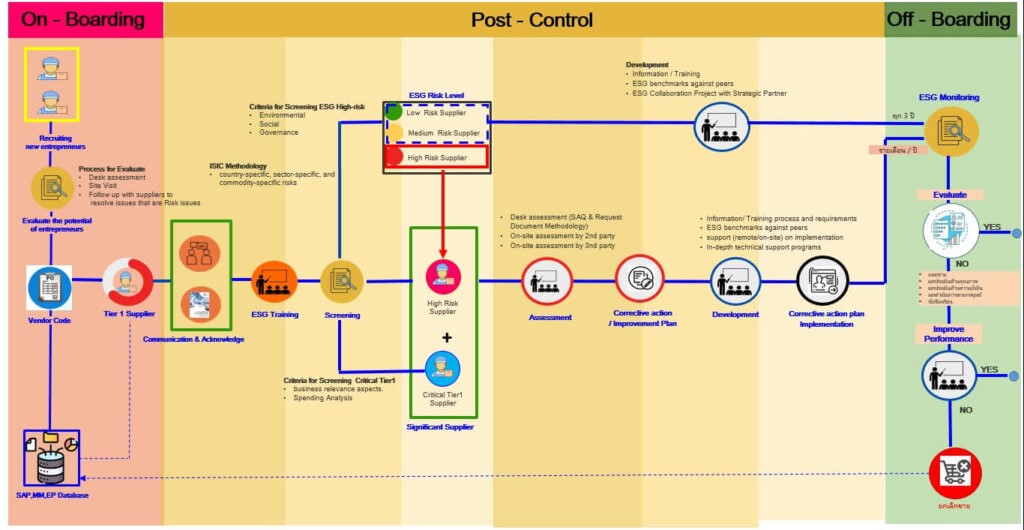
Identifying Significant Tier-1 and Non-Tier-1 Suppliers

Tier 1 Suppliers

Significant Tier 1 Suppliers*

Significant Non-Tier 1 Suppliers
*Note: The company identifies significant suppliers based on as follows:
1.Suppliers with Significant Business Relationships – Suppliers that pose a risk due to the Company’s dependency, including:
– Suppliers with high purchase value
– Suppliers impacting competitive advantage and market success
– Suppliers that are irreplaceable or have limited alternatives
2.Suppliers with High ESG Risks – Suppliers that have a high risk of causing negative environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts
Supplier Identification and Spending Analysis
Spending value (million Baht) categorized by spending source
Total spending with Tier-1
suppliers – Domestic
Total spending with Tier-1
suppliers – Significant suppliers
Total spending with Tier-1
suppliers – SMEs*
*Note: Total spending with SMEs includes agricultural products, community products, and community enterprise products
Tier-1 Suppliers Engagement
Communicated for Suppliers’
Code of Conduct*
Written Acknowledgement for
Suppliers’ Code of Conduct*
Tier-1 suppliers participate
in the ESG risk screening program
*Remark: Target 2024: 100%
Engagement of Significant Tier-1 and Non-Tier-1 Suppliers
Communicated for Suppliers’ Code of Conduct*
Written Acknowledgement for Suppliers’ Code of Conduct*
Significant suppliers participate in the ESG risk assessment program
ESG-impacting suppliers participate in the supplier development program
*Remark: Target 2024: 100%
Managing risks of significant Tier-1 and Non-Tier-1 suppliers
Suppliers assessed via
desk Assessment or Onsite Assessment
Percentage of a negative impact on all suppliers assessed
Suppliers Assesses with Substantial
Actual/Potential Negative Impacts
Suppliers with Substantial Actual/Potential Negative Impacts that were Terminated
Total suppliers with Substantial Actual or Potential Negative Impacts with Agreed Corrective Action/Improvement Plan
Total Suppliers Supported in Corrective Action Plan Implementation
Suppliers are supported in capacity building to reduce impacts according to the corrective action plan
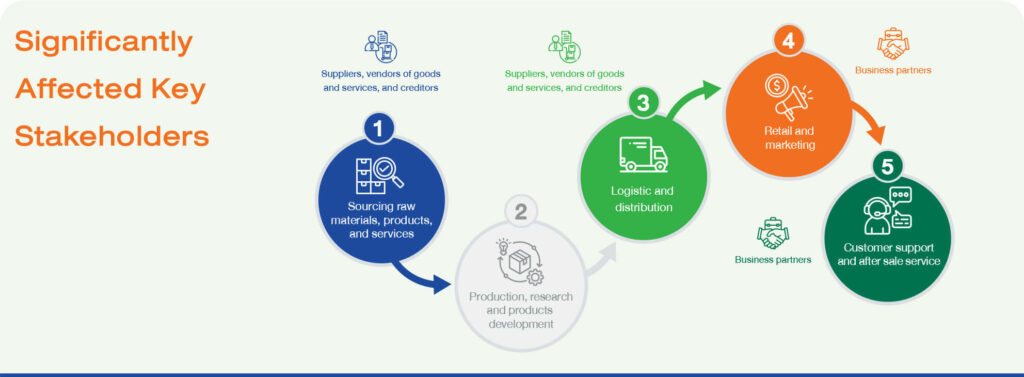
Risks and Opportunities
In 2024, businesses must rapidly adapt to meet consumer demands for convenience and speed in purchasing and consuming products. The adoption of new technologies in the supply chain, such as artificial intelligence (AI) for warehouse and logistics data analysis, is essential. However, inefficient use of technology-due to a lack of knowledge, poor planning, or system integration issues-can lead to delays or disruptions in delivery processes. Additionally, business partners may face pressure to adapt to market and technological changes. These risks could result in consumers not receiving the expected experience and may negatively impact the business’s long-term credibility.
Additionally, responsible supply chain management enhances production quality and improves the efficiency of product and service delivery to consumers, with business partners playing a crucial role in the supply chain. Selecting capable suppliers, developing their competencies, and fostering engagement through sustainable collaboration programs help mitigate various risks, such as rising costs, raw material shortages, and human rights violations.
The Company is committed to enhancing the potential of all business partners for sustainable growth, considering social, environmental, governance, and human rights factors throughout the supply chain. The goal is to create business opportunities, mitigate risks, and strengthen competitiveness while driving positive change that reinforces the resilience of suppliers and business alliances.
Management Approach
The Company integrates sustainable procurement policies, supplier ethics guidelines, and social and environmental considerations into supply chain management. The focus is on maximizing efficiency with transparency, fairness, and respect for human rights, covering key areas such as human rights, business ethics, environmental standards in production processes, and sustainability of supplier products and services. Additionally, the Company encourages all supplier groups to adopt sustainable and responsible procurement policies to minimize negative impacts on stakeholders. The Company also promotes collaboration with Tier-1 suppliers and significant subsequent suppliers in sustainable operations.
The Company conducts risk screening for all Tier-1 suppliers using criteria that encompass environmental, social, governance (ESG), and business significance dimensions. In the screening process for significant suppliers, the Company considers factors such as high purchase value, strategic importance, limited supplier availability, and irreplaceable suppliers, along with suppliers that may pose negative ESG impacts based on country, industry, and product-specific risks. By assessing these risks, the Company can identify significant suppliers and conduct assessments to mitigate supply chain management risks.
Additionally, the Company focuses on improving quality of life and fostering strong relationships with communities and society while actively participating in mitigating environmental and ecological impacts in alignment with the Company’s sustainable supply chain management policies and goals.
Corporate Supply Chain Management Strategy
Provisions, procurement, contracting, procurement management of equipment, products, services, and construction according to specifications at the highest level of service (product quality, cost, after-sales service, and delivery)
Integrated demand and supply chain management (through balancing data utilization and reflecting on cost and supply management)
Develop and co-create innovative products, services, and equipment with partners/suppliers to increase variety and operational efficiency
Strengthen strategic alliances and manage sustainable business partnerships
Ethics and Guidelines for Suppliers
The Company is committed to encouraging suppliers to conduct business responsibly by supporting their compliance with the suppliers’ code of conduct and guideline, which applies to Tier-1 suppliers and Critical Non-Tier-1 suppliers throughout the supply chain. This guideline consists of 16 key practices. In 2024, the company communicated the Supplier Code of Conduct and Guidelines to 2,412 Tier-1 suppliers, both existing and new, representing 100% of all suppliers. To ensure effective operations, the Company has conducted Buyer Development Training on Sustainability Procurement for relevant employees. This training aims to raise awareness and understanding of the updated 2022 suppliers’ code of conduct at all levels, providing a framework for sustainable supply chain management.
Sustainable Supply Chain Management Process
| Sustainable Supply Chain Management Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrate the concept of sustainability, reduce risks throughout the supply chain | Value and Develop Creation Support SMEs | ||
01 Communicate expectations, recruit, and select capable suppliers while considering sustainability criteria |
02 Supplier sustainability risk management (screening and assessment) |
03 Promote and support capabilities development |
04 Build and maintain a long-term relationship |
1. Communicate expectations, source, and select potential suppliers
The Company selects suppliers responsibly and efficiently by integrating sustainability considerations into every stage of the sourcing and selection process for new suppliers. The Company has established evaluation criteria for assessing supplier potential and qualifications, covering key aspects such as:
Product quality and safety

Compliance with legal and regulatory
requirements

Production capability and cost management
efficiency

Delivery capability and sustainability performance (ESG), based on supplier selection scores according to the Company’s sustainability criteria
Suppliers who do not meet the minimum score criteria and fail to improve their sustainability performance within the specified timeframe will not be considered for contract renewal. Additionally, the Company communicates expectations through the suppliers’ code of conduct and guidelines to ensure suppliers are informed and adhere to these standards.
The Company continuously reviews and improves its procurement practices to align with the suppliers’ code of conduct and guidelines while mitigating risks associated with non-compliance with the organization’s ESG requirements. Emphasizing sustainable procurement, the Company conducts training sessions to raise awareness among executives and employees involved in supplier selection and procurement, as well as external stakeholders such as contractors and business partners.
In 2024, a total of 189 new suppliers, accounting for 100 percent, were selected based on criteria integrating sustainability considerations. These criteria encompass environmental, social, and human rights aspects, as well as governance and economic factors.
2. Managing sustainability risks for suppliers (screening and assessment)
Screening significant suppliers
Companies recognize the significance of supplier screening as a crucial step in identifying and assessing potential risks associated with partnering with each supplier. These risks can encompass financial instability, product quality issues, operational disruptions, legal compliance concerns, and reputational damage. By proactively identifying these risks, companies can make informed decisions regarding supplier selection, develop effective risk management strategies, and mitigate potential negative impacts on their business operations.
To ensure sustainable growth and mutual success with its partners, the company has implemented a systematic, continuous, and annual supplier screening and risk assessment process. This comprehensive approach aims to enhance the performance of each supplier, fostering a collaborative environment for long-term growth. The process entails the following key steps:
| Supplier Assessment Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manage Supplier’s Sustainability | Promote and support capacity development | ||
| Supplier Screening and Identify Significant Suppliers | Supplier Assessment | ||
| – Screen suppliers using ESG indicators (Environmental, Social, Governance) and Business relevance – Methodology for suppliers screening by country-specific risk, sector-specific risk, and commodity-specific risks – Identify Significant Tier1 suppliers |
– Methods of Supplier Assessment (1) desk assessment (2) on-site assessments by 2nd party (3) on-site assessments by 3rd party – Audit procedure using SMETA standards – Assessment Results and Corrective Actions |
– Supplier information and trainings – ESG benchmarks against peers – Support on implementation of corrective action plan – Support programs to build capacity and ESG performance |
|
The Company places importance on thoroughly screening suppliers by evaluating all Tier 1 and Non Tier 1 Suppliers, including both existing and new suppliers, to identify those that are significant to the business. This screening process is carried out jointly by the procurement department and the supply chain risk assessment unit, which continuously evaluates suppliers’ preliminary risks. The evaluation considers two key factors: 1) Business relevance, assessed through two sub-factors: high spending (significant purchase value) and non-substitutability (difficulty in replacing the supplier), or their essential role in the Company’s production and operations. 2) ESG risk, covering environmental, social, and governance concerns.

Environmental: E

Social: S

Governance: G

Business Relevance
The Company evaluates the significance of suppliers to the business alongside their level of sustainability risk (ESG Risk). The sustainability risk associated with a supplier’s business operations is assessed based on various relevant factors, including:
The Company integrates business significance and sustainability risk assessment results to identify significant suppliers. Suppliers with high business importance and high sustainability risks are classified as significant suppliers through the screening process. In 2024, the Company identified 263 significant Tier-1 suppliers, and 17 significant non Tier-1 suppliers, with all significant suppliers totaling 280, representing 11.53% of all suppliers. Additionally, the Company regularly reviews supplier evaluations annually to ensure accurate and appropriate classification of significant suppliers.
Key issues identified in sustainability assessment
| (Environmental : E) | |
|---|---|
| Non-Conformity Issue | Mitagation Plan |
| Environmental Management – The operation shall be in accordance with the Energy Conservation Promotion Act B.E. 2535 (1992) |
– Review the relevant legal provisions regarding energy conservation promotion and take actions in accordance with the law |
| (Social : S) | |
| Non-Conformity Issue | Mitagation Plan |
| Labor management and human rights – Employee Health Check-up Based on Risk Factors – Health Book |
– Prepare a Health Check-up Manual Based on Risk Factors and Conduct Employee Health Check-ups – Create a Health Book for Employees |
| Occupational safety and health – Organize training on “Firefighting and Fire Escape Training and Chemical Spills” for employees – Inspection of operating environment – Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment |
– Plan and organize annual training and prepare a training report – Prepare an annual inspection plan for the operating environment by the agency that has been certified – Analyze inspection results and improve and correct according to the law – Establish a plan and practices for occupational health that comply with legal requirements, such as risk assessment |
| (Governance : G) | |
| Non-Conformity Issue | Mitagation Plan |
| Compliance with laws and regulations – Monitor changes in laws related to business operations – Labor Handbook – Employment Contract – Evidence of Compensation Payment – Conduct “Occupational Health and Safety Officer” Management Training – Registration of Personnel or Organizations in Occupational Safety at the Management Level, Supervisors, etc. |
– Designate responsible individuals – Create a legal register and track changes in various laws – Prepare a Labor Handbook and communicate it to employees – Prepare a written employment contract in a language that is easily understood by employees – Prepare written documentation of compensation payments – Appoint safety personnel at various levels, send them for training, and notify the registration with the Department of Welfare and Labor Protection |
Assessment of Significant Suppliers to Business
The Company employs various supplier assessment methods to ensure accurate, comprehensive, and appropriate information based on the supplier’s business size, as follows:
Desk Assessment
Desk Assessment is a process conducted by the supply chain sustainability assessment unit by gathering essential data for evaluating business partners from various sources, including: 1) Supplier Self-Assessment – Suppliers must fill out information such as general company details, ESG policies and management approaches, risk management, and various performance results. 2) Relevant Documents and Reports – These include financial reports, sustainability reports, or various certification documents that suppliers may be requested to submit. And 3) Public Databases – Information that suppliers have disclosed publicly. The supply chain sustainability assessment unit then analyzes the collected data to assess risks associated with the supplier and ensure that the supplier has appropriate measures in place to manage those risks.
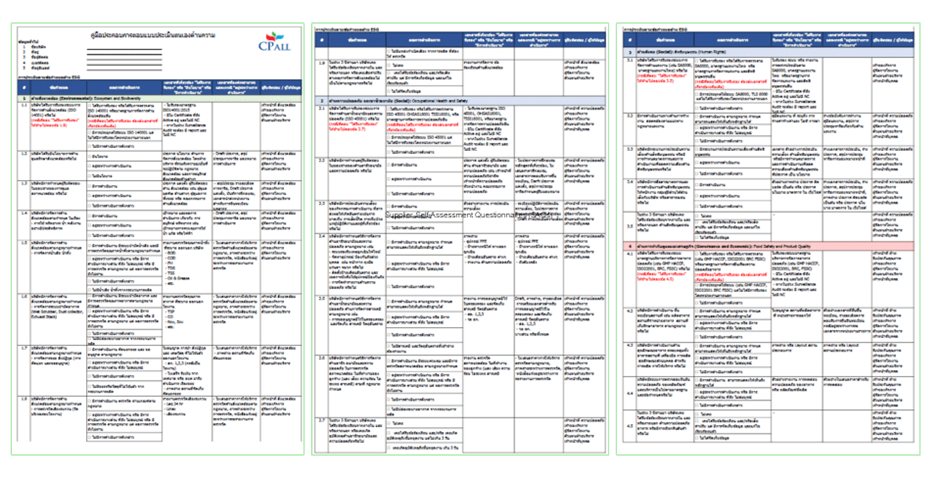
On-Site Assessments by 2nd Party
In cases where suppliers are unable to provide evidence or risk management measures, the Company will conduct supplier assessments through on-site evaluations by the internal Quality Assurance department (2nd Party Assessment) to identify exisiting risk issue. The risk assessment checklist is designed in alignment with internationally recognized standards and best practices, such as the SMETA standard, which covers human rights risk issues, including labor standards, discrimination, employment and compensation practices, health and safety, environmental impact management, business ethics, and the traceability system for raw materials through to finished products.

On-Site Assessments by 3rd Party
The Company places great importance on strict supplier assessments, particularly for Critical Tier-1 Suppliers that export products internationally. These suppliers are required to undergo an ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risk assessment conducted by independent external experts to ensure compliance with international standards, such as ISO 14001, ISO 54001, SA8000, ISO 45001, ISO 22000, ISO 22301 (BCM), and ISO 50001.

In addition, CP ALL hires an accredited external independent agency (Third Party) to assess significant suppliers using international standards, such as SMETA, for supplier evaluations, ensuring that monitoring and assessments are conducted efficiently. the Company will request suppliers to provide audit results and certifications from independent bodies for use in Surveillance Audits. This information will be reviewed to assess ESG risk management practices and evaluate supplier performance, ensuring that suppliers meet both the Company’s requirements and international standards.
In 2024, the company conducted assessments of 263 significant Tier-1 suppliers and 17 significant non Tier-1 suppliers, totaling 280 suppliers. It was found that 20 suppliers had actual or potential significant negative impacts, representing 7.14% of all significant suppliers, across 47 issues.
The Company also encourages suppliers to establish their own sustainability risk management measures. Suppliers with actual or potentially significant negative impacts have developed corrective action plans or improvement plans in accordance with the agreement, accounting for 100%.
The Company continuously monitors suppliers’ risk management progress while supporting their development and capacitybuilding to enhance efficiency and promote sustainable business growth alongside organizational development. In 2024, suppliers receiving support in implementing corrective action plans accounted for 100%, while Significant Tier-1 and non-Tier-1 suppliers receiving capacity development support accounted for reduce impacts according to the corrective action plan, representing 100 % (20 suppliers).
3. Promote and support capacity development
The Company is committed to continuously enhancing suppliers’ capabilities, enabling them to apply the knowledge and skills acquired to further their sustainable business operations. Various initiatives have been implemented to support this goal, such as training programs delivered through online and offline channels. These programs cover topics including responsible and sustainable business operations in alignment with ESG principles, business ethics development processes and best practices for suppliers, and examples of good practices for sustainable operations.
Supplier Information/Trainings on Company’s Supplier ESG Program, Process, and Requirements
The Company communicates and shares ESG knowledge with suppliers through the following initiatives:
In 2024, the Company implemented various initiatives to enhance suppliers’ sustainability knowledge and capabilities, with notable project as follow:
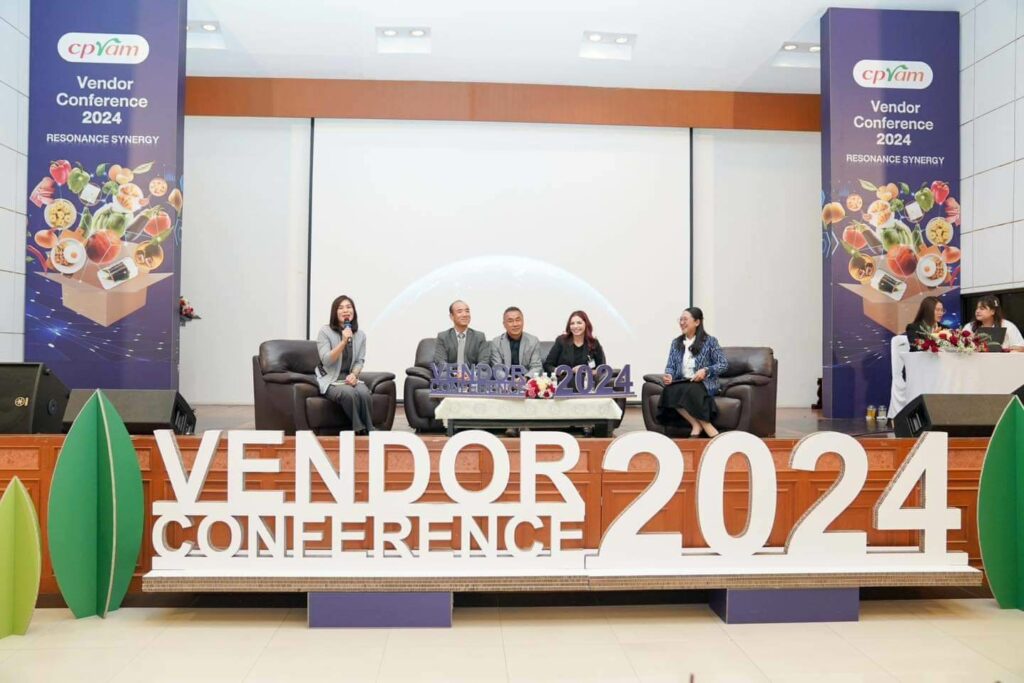
Ongoing Project: “Vendor Conference 2024”
CPRAM hosted the “CPRAM Vendor Conference 2024” under the theme “RESONANCE SYNERGY: Uniting Strengths for Unity.” The event reflects the company’s commitment to fostering strong relationships with suppliers and partners as strategic allies. It also aimed to communicate the organization’s policies and growth direction, while providing a platform for knowledge exchange. The conference featured discussions on topics such as “Opportunities for Sustainable Business Development,” “Global Quality Standards,” and a lecture on “Sustainable Development Goals – ESG.” This collaborative effort is focused on advancing sustainable development in the areas of ESG: Environment, Social, and Governance, promoting sustainable business practices, and creating strong, mutual understanding between the organization and its strategic partners. Over 200 key partners, as strategic allies, attended the event, sharing a vision for growth and sustainability.
Ongoing Project: ALL Delica Alliance (ADA) – Year 2
CPRAM is committed to continuously developing appropriate technologies and innovations throughout the value chain. The Company has established the ALL Delica Alliance (ADA), a sustainable food partnership, to implement the FOOD 3S concept (food safety, food security, and food sustainability) with the goal of efficiently managing the food supply chain and covering nutritional care for the elderly.
Additionally, the Company shares knowledge and expertise from business management specialists in various fields, such as product development, marketing, process improvement, quality assurance, and cost management. It also places importance on safety and the environment to promote the stability and sustainability of business partners, as well as driving continuous innovation and development.
This approach, the company is committed to contributing to the development of the economy, society and the supply chain system to grow steadily and sustainably.
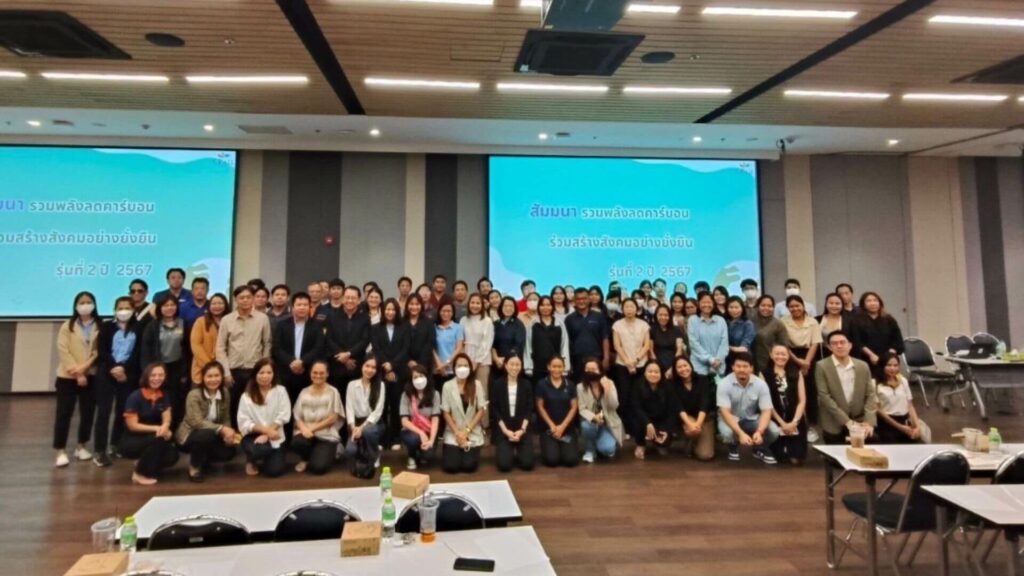
Seminar on “Uniting to Reduce Carbon Emissions for a Sustainable Society”
The Company is committed to sustainable growth under the “2 Reductions, 4 Creation, 1 DNA” strategy, emphasizing the reduction of plastic and energy consumption in line with the “7 Go Green” policy to continuously protect the environment 24 hours a day. The Company has set targets to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030 and net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
To prepare suppliers for achieving these goals, the Company organized a seminar for 117 suppliers on transitioning towards carbon neutrality and net-zero emissions. The seminar covered topics such as greenhouse gas accounting, the importance of net-zero targets, current environmental challenges, and future related regulations. Additionally, tools and templates were introduced to help suppliers identify greenhouse gas emission sources and develop effective emission reduction plans.
Seminar participants exchanged views and discussed relevant issues to collectively promote environmental stewardship in line with CP ALL’s “Giving & Sharing” commitment to creating a livable and sustainable world.
Supplier Access to ESG Benchmarks Against Peers
Suppliers will receive information and tools to compare their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance with other suppliers in the same industry, as follows:
Supplier Support (Remote/On-site) on Implementation of Corrective Actions
The Company provides support to suppliers in implementing corrective measures to address identified issues or deficiencies, as follows:
In-depth technical support programs to build capacity and ESG performance in suppliers
In-depth technical support programs to build capacity and ESG performance in suppliers. The Company recognizes the importance of enhancing suppliers’ capabilities to ensure sustainable operations in compliance with its ESG standards and to promote long-term sustainable growth. To achieve this, the Company has implemented training programs to strengthen suppliers’ capabilities and has established an annual performance assessment to measure progress. In 2024, the Company carried out the projects as follows:
In-depth technical support programs to build capacity health & safety management topic for transportation contractor
Sustainability risk results analysis of suppliers (Non-Compliance (Potential Fact Finding: PF)) according to the law revealed common risks issues in 2024 inclusive of occupational safety and health.
The Company has therefore developed programs to provide in-depth technical support to improve occupational health management potential and safety in logistics and develop in-depth safety management potential for logistics contractors. This approach raises transportation vehicle safety standards for vehicles involved in Company operations. Plans to regularly monitor progress from 2022-2025 are as follows:
 7% 7%
| |
Impacts and Benefits

Logistics contractors gain better transportation safety comprehension

Transportation accidents reduction
4. Strengthening and maintaining relationships with suppliers
The Company is committed to strengthening suppliers for sustainable growth together by maintaining strong relationships through various activities, including 1) organizing seminars and policy direction briefings, as well as conducting annual supplier visits to facilitate discussions and mutual feedback, 2) developing joint business plans with strategic suppliers by exchanging data, analyzing market trends, and co-developing business growth strategies to ensure alignment and operational efficiency, 3) sharing knowledge and exchanging essential business development information, as well as implementing collaborative projects and initiatives to enhance supplier capabilities in all aspects, 4) promoting sustainability through initiatives such as developing eco-friendly packaging and systematically managing post-consumer packaging to minimize environmental impact, 5) supporting access to technology and innovation to enhance product value in line with market demands and consumer behavior, and 6) continuously improving supplier operations within the supply chain to ensure competitiveness and sustainable growth.
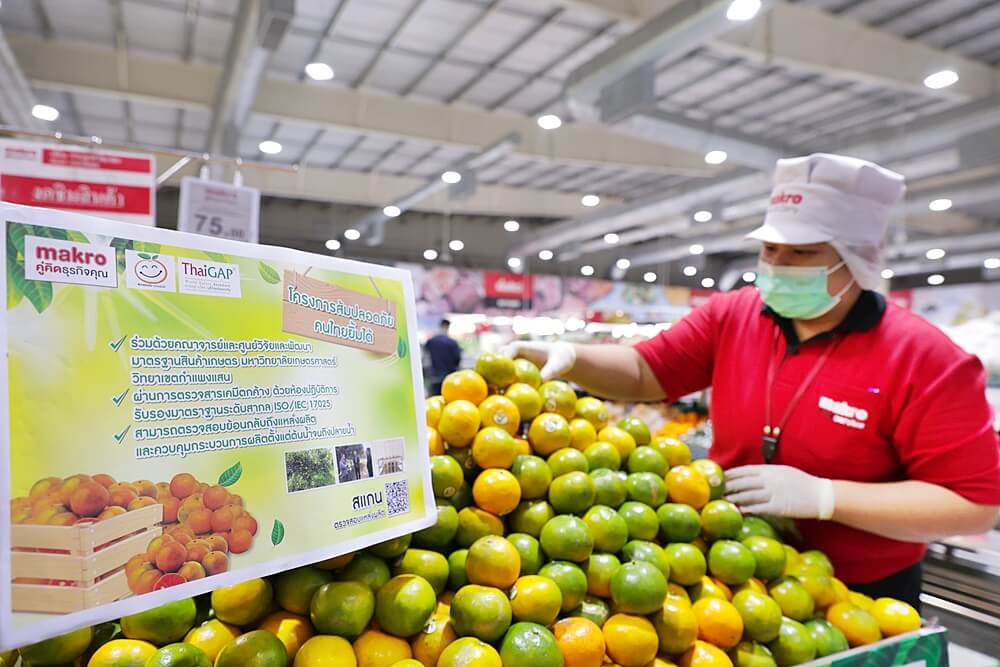
Ongoing Project: “Safe Oranges, Smiling Thais” – Year 11
CP Axtra collaborates with Kasetsart University, Maejo University, and the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives to develop the “Safe Oranges, Smiling Thais” project. This initiative focuses on transitioning orange farmers to Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) by encouraging them to stop using chemical pesticides and adopt local herbal alternatives instead. The project also ensures pesticide residue testing through certified laboratories and utilizes an application for traceability. Customers can verify the source of production using the Makro i-Trace QR Code, available on packaging or display stands.
Impacts and Benefits

Farmers
participated in the project
Covers area
from a total of 7 provinces
Annual procurement exceeds
ESG Integration in SCM Strategy
The Company has integrated ESG in SCM strategy as follows:
| Key objectives | ESG-related objectives in supply chain management | Overall supply chain management strategy linking to ESG |
|---|---|---|
 Empowering SMEs |
Enhance SMEs capability in diffe rent perspectives, e.g. financial, product development, packaging development, logistics, sustainability, etc. Our supply chain management focuses on co-creation initiatives according to SDG 8.2, Striving for results entails creating positive economic impact alongside improving the quality of life of society and communities |
Create shared value “development and promotion of SMEs”, CP ALL is committed to improving the potential of business partners, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, by providing training, consulting and advice on standard inspections. Root management Including co-inventing innovations to create efficiency in treatment Environment and friendliness to society and community |
 Reducing plastic waste from packaging |
Reduce volume of packaging usage from suppliers within the general waste management process, consistent with CP ALL’s circular economy goals. This aims to fulfill SDG 12.6 and CP ALL Sustainability Framework “Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection” through packaging design, materials, and reduction programs. through packaging design selection of materials with an aim to reduce the amount of plastic waste packaging development project, to be friendly to the ecosystem and environment |
7 Go Green “environmentally friendly packaging” reduces the use of plastic in packaging and integrates sustainability concepts into various operations, especially in packaging design and material selection. The joint projects between packaging suppliers include developing processes which reduce the amount of material used, etc. |
In addition, the Company has applied the sustainability criteria to assess the risks of its existing and new suppliers manufacturing Private Brand: PB products whereby suppliers must undergo sustainability risk assessments through the Suppliers Self-Assessment Questionnaires (SAQ) system. Selected suppliers meeting Company criteria standards must score a minimum of 50% on sustainability performance. The established Company established sustainability criteria include product and production standards, employment, welfare, and environmental management.
Supply Chain Management’s Success Indicators
The Company has set the index to measure the success of supply chain management. In 2024, there are indices that measure success goals, and operating results as follows:
| Supply Chain Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Target | Performance for the previous 3 years |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 Suppliers considered Significant Suppliers in terms of sustainability must be proactively audited (Comprehensive Assessment) for development and improvement | 100% of Tier 1 Suppliers with high sustainability risk must receive comprehensive assessment and improved by 2030 | |
| Procurement spending on SMEs | Procurement spending on SMEs increased by 10% by 2025 (compared to base year 2020) | |
| Supplier Engagement | 80% for supplier engagement level by 2030 | |
| Plastic packaging within the Company’s control (Private Brand) must be reusable or reused or biodegradable | 100% of plastic packaging within the Company’s control (Private Brand) must be reusable or reused or biodegradable for companies operating in Thailand by 2025 and for companies operating overseas by 2030 |
Related Policy and Guideline
| News and Activities | Visit Page |
| Sustainable Sourcing Policy | Download |
| Supplier Code of Conduct and Guideline | Download |












